
You want your digital ads to reach the right people, and you also want them to see your ads at the right place and time. Almost 90 percent of marketers use location-based ads, often leveraging geofencing for targeted campaigns to enhance precision. You must choose between geofencing or geotargeting based on your goals and specific situation. Many marketers face challenges like privacy concerns and worries about data accuracy. Additionally, rules and laws can complicate the process.
Common Challenges in Location-Based Advertising | Explanation |
|---|---|
Privacy Concerns | Laws require permission and transparency. |
Data Accuracy | Outdated location data can reduce ad effectiveness. |
Systems demand skilled personnel and careful planning. |
Consider how precise you want your ads to be and how many people you aim to reach. Also, decide how quickly you want your ads to take effect. These factors will help you select the best strategy for your campaign, especially when using geofencing for targeted campaigns.
Key Takeaways
Geofencing finds people who are very close to a place by using GPS. This is good for quick ads about store sales or events.
Geotargeting covers bigger places like whole cities by using IP addresses. It helps you show ads to lots of people and saves money by picking the best spots.
Pick geofencing if you want to talk fast to people near your store. Pick geotargeting if you want to reach more people with special messages.
Both ways have privacy rules. You must get permission, keep data safe, and tell customers what you do. This helps people trust you and keeps you legal.
Using geofencing and geotargeting together can help your campaign. You can reach many people and also send special deals to those who are close by.
Geofencing and Geotargeting Basics

What Is Geofencing?
Geofencing lets you set up a digital border around a place using GPS. When someone with a phone goes in or out, you can send them ads or messages. This helps you reach people at the right spot and time. For example, you can give a deal to shoppers as they enter your store. Geofencing is good for being exact and fast. It works well if you want to target people very close by. You can use it to get more people in your store and make them more interested. It can also help you earn more from your ads. Geofencing and geotargeting both use location data to find people. But geofencing is better when you need to be very precise.
Tip: Geofencing is best for reaching people near your store or event right away.
What Is Geotargeting?
Geotargeting uses IP addresses to find people in bigger areas like cities or zip codes. You can also use other info, like age or interests, to pick who sees your ads. Geotargeting helps you talk to more people and change your message for where they live or work. For example, you can show hotel ads to travelers in a certain city. Both geofencing and geotargeting use location to market, but geotargeting is better for bigger campaigns. It lets you save money by showing ads only in the right places.
Here’s a simple chart to show how geofencing and geotargeting are alike and different:
Aspect | Geofencing | Geotargeting |
|---|---|---|
Location Detection | Uses GPS to make a digital border around a place | Uses IP address to find bigger areas like cities |
Targeting Precision | Very exact, finds people who enter the border | Less exact, finds people in large areas |
Engagement Method | Finds people right away and sends messages fast | Shows ads based on where people are and their info |
Marketing Focus | Focuses on being exact and close to the business | Focuses on being flexible and reaching more people |
Both geofencing and geotargeting are important for ads that use location. They both help marketers use where people are to get better results.
Key Differences
Scope and Precision
Geofencing and geotargeting are different in how they find people. Geofencing looks at small places like a store or event. Geotargeting covers bigger places like a city or region. The table below shows how they are not the same:
Aspect | Geotargeting | Geofencing |
|---|---|---|
Scope | Broader geographic areas (e.g., cities, regions) | Narrow, specific physical locations (e.g., stores, venues) |
Precision | Less precise, targets general location data | Highly precise, targets users entering/exiting boundaries |
Action Orientation | Passive use of location data to tailor content | Active triggers based on user movement relative to geofence |
Typical Use Cases | Regional marketing campaigns, content customization | Immediate, location-specific marketing (e.g., instant offers) |
Geofencing can send ads when someone enters or leaves a spot. Geotargeting shows ads to people in a bigger area, but it cannot find their exact spot. If you want to give quick deals to shoppers near your store, geofencing is best. Geotargeting is better if you want to reach more people in a city.
Technology Used
Geofencing and geotargeting use different tools. Geofencing uses GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or RFID to make digital borders. These tools help track when a device goes in or out of a place. Geotargeting uses IP addresses and cell data to find people in large areas. Geofencing is more exact because it can find a device within about 50 meters. Geotargeting is less exact because it only knows the general area, like a city or zip code. Geofencing is better for exact ads, but geotargeting helps you reach more people.
Data and Privacy
Geofencing and geotargeting collect different data. Geofencing gets exact info like when a device enters or leaves, how many people walk by, and how long they stay. Geotargeting collects bigger data, like what people do in a region and who lives there. You need to think about privacy when using these tools. Some people do not know their location is tracked. Laws like GDPR and CCPA say you must get permission and keep data safe. You should be clear, collect only what you need, and let people opt out. This helps you build trust and follow the rules.
Geofencing for Targeted Campaigns
How Geofencing Works
Geofencing lets you set a digital border around a real place. This area can be small like a store or big like a stadium. When someone with a phone goes in or out, you can send them ads or deals. Geofencing uses GPS, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth to know when a device crosses the line. This helps you reach people right when they are close to your business or event.
Geofencing gives you real-time contact and better accuracy. You can see how many people answer your message and check if your ads work. Many brands get more customer interest when they use geofencing for targeted campaigns.
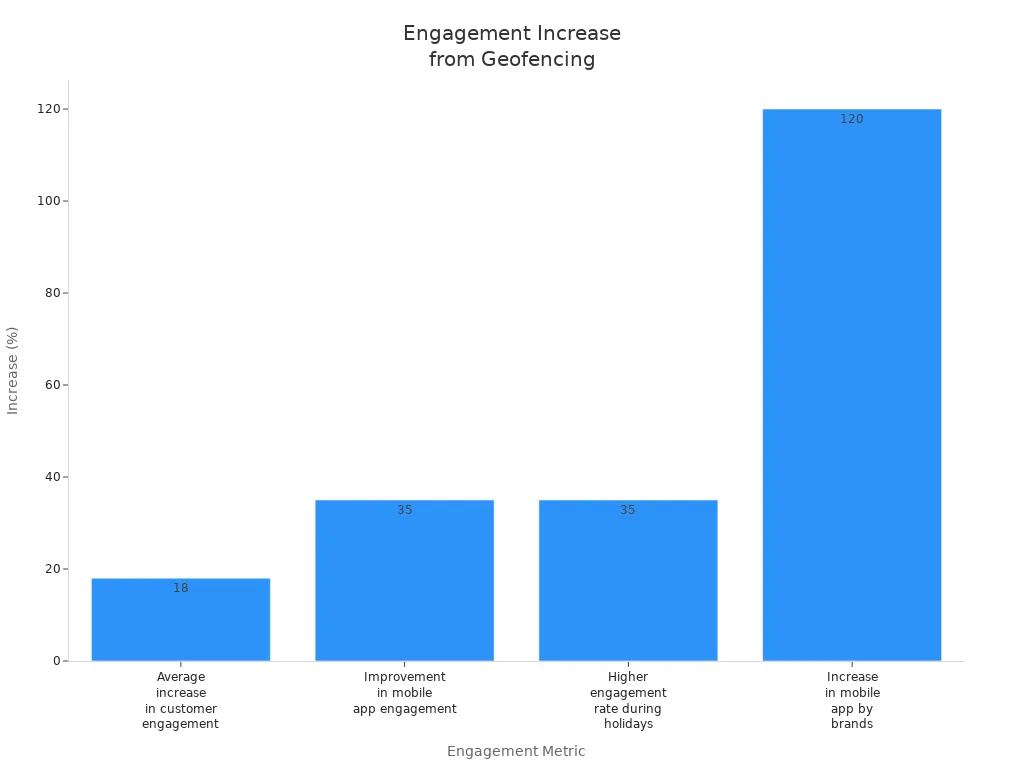
Metric Description | Reported Increase in Engagement |
|---|---|
Average increase in customer engagement | 18% |
Improvement in mobile app engagement | 35% |
Higher engagement rate during holidays | 35% |
Increase in mobile app engagement (brands) | 120% |
Note: Geofencing for targeted campaigns can help some brands get up to 120% more mobile app use, especially during busy times.
Best Use Cases
Geofencing works best for businesses that need local customers and quick offers. Stores use geofencing to send deals when people walk in or pass by. Fast food places get customers from other places by giving instant deals. Event planners remind people near the event to come in. Rideshare companies like Uber use geofencing to help with pickups at airports and busy places.
Here are some top benefits of geofencing for targeted campaigns:
You can reach local customers at the right time and place.
You can get more people to visit your store and buy things.
You can learn about what customers do in each spot.
You can give special deals based on where people go.
You can see how well your ads work in the real world.
Industry | Example Companies/Brands | Geofencing Use Case and Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|
Quick-Service Restaurants | Burger King, Taco Bell, Dunkin’ | Burger King’s ‘Whopper Detour’ got 1.5M app downloads by targeting McDonald’s; Taco Bell had a 6% sales jump and 20% more spending from app orders after geofenced alerts; Dunkin’ got more people in stores with location-based deals. |
Coffee & Beauty Retail | Starbucks, Sephora | Starbucks uses geofencing for special deals and rewards; Sephora makes shopping better with app alerts and tips. |
Big-Box Retail & Travel | Walmart, HotelTonight | Walmart uses geofencing for curbside pickup; HotelTonight sends last-minute hotel deals based on where users are. |
Rideshare Services | Uber | Geofencing helps Uber with pickup spots and wait times at busy places like airports, making rides easier to get. |
Healthcare Recruitment | Johns Hopkins Hospital | Finds healthcare workers at events and other hospitals using geofenced ads. |
You can see geofencing helps many local campaigns, from stores to hiring. Geofencing and geotargeting can both be used, but geofencing is best when you want fast action in one place.
Geo-Targeting Strategies
How Geotargeting Works
Geo-targeting lets you show ads to people by where they are. It uses data from IP addresses, GPS, Wi-Fi, and sometimes geofencing. You can reach people in cities, regions, or even small neighborhoods. You can also use other details like age or interests to make your ads fit better.
To run a good geotargeting campaign, you should:
Pick places that match your audience and where they are in the sales funnel.
Use tools like IP targeting, GPS, Wi-Fi, or geofencing.
Change your ad for each place to make it more useful.
Make landing pages with local keywords and local SEO.
Test which places work best and leave out places that do not help.
Use geo-targeting options on Google Ads or social media.
Make offers for each location and watch your campaign to make it better.
Note: Geo-targeting helps you change your ads fast. You can reach the right people at the right time. You save money by showing ads to fewer people who are more likely to buy.
Best Use Cases
Geo-targeting is used a lot in digital marketing. It works for local shops and big brands. You can send offers to people near your store. You can get more people to visit your shop. You can show ads in the right language and style for each place.
Some top ways to use geotargeting are:
Personalizing messages for people based on where they are.
Changing campaigns for different places to save time.
Testing ads and deals for each region or time zone.
Showing ads near your competitors’ locations.
Helping people find things in your store and giving local tips.
Geo-targeting does more than just reach people. It makes ads more interesting and gets more people to buy. You also get better results and save money. For example, Domino’s Pizza got 400% more return on investment with geotargeting. Most clients get 4.5 times more ROI from geo-targeting.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Quantitative Example | Domino’s Pizza got 400% more ROI with geotargeting (June 2023 data). |
Average ROI Claim | Clients get an average of 4.5 times more ROI from geotargeting. |
Qualitative Impact Statement | Geo-targeting helps you show ads to fewer people, spend less, and get more sales. |
Geo-targeting gives you many good things like better ads, more sales, and less wasted money. It is a strong tool for your digital strategy. When you look at geofencing and geotargeting, you see geo-targeting works for both small and big campaigns.
Pros and Cons
Geofencing
Geofencing is great for ads that need to be very relevant. It lets you find people who cross a digital line near a place. You can send them messages or deals right away. This helps you get more people in your store and sell more. Geofencing uses location data, just like geotargeting. But geofencing is more exact and fast. You reach people when they are close to your store or event.
Geofencing lets you make special experiences for customers. It helps you get more interest from them. You can see results quickly and change your ads to do better.
Geofencing also has some problems. You must spend time making ads for each place. Your ads only show to people who let apps use their location. This means fewer people see your ads. Bad GPS signals can make people miss alerts or get wrong ones. Geofencing uses a lot of battery because GPS stays on. Some people worry about privacy since you track where they go. If you want to cover many places, it can be hard and slow.
Benefits of Geofencing | Disadvantages of Geofencing |
|---|---|
Very exact and fast targeting | Takes a lot of time to set up |
Gets more people in your store | Not many people see your ads |
Quick contact with customers | GPS can be wrong sometimes |
Special deals for each person | Uses up phone battery |
Fast way to check results | People worry about privacy |
Geotargeting
Geotargeting helps you reach people in big areas like cities. You can change your ads for each place and use things like age or hobbies. Geofencing and geotargeting work together for local and big campaigns. Geotargeting is easier to use for many places. It saves money by showing ads only where you want.
Geotargeting has some problems too. If you target too much, you might not reach enough people. If you do not change your ads for each place, people may not care. If you do not change your bids for each area, you can waste money. Sometimes, IP addresses or VPNs show ads to the wrong people. People also worry about privacy when you use their location. You need more time and work to make ads for each place. If you target too many or too few people, you might not get good results and your brand can get confusing.
Benefits of geotargeting:
Reach lots of people
Easy to change and manage ads
Save money with location ads
Simple to use for big campaigns
Disadvantages of geotargeting:
Might target too much
Hard to make ads fit each place
Lose money if ads go to wrong people
Geofencing and geotargeting both have good and bad sides. Pick the one that fits your goals and the people you want to reach.
Choosing the Right Approach

Campaign Goals
You should pick your marketing plan based on your goals. Geofencing and geotargeting do different things. If you want more people in your store or want many people to know your brand, geofencing is a good choice. This tool lets you reach anyone who walks into a certain place, like a shop or event. You can send them deals or alerts right away, which helps you talk to them fast.
If you want to get more sales by reaching a certain group, geotargeting gives you more control. You can use things like age or what people like to show special ads. For example, if you rent boats, you can show ads to people who like water sports in one zip code. Geotargeting helps you spend your money better and get more people interested. You can try different ads for each group and change your plan to do better.
Tip: Use geofencing when you want to reach lots of people in one area fast. Use geotargeting when you need to pick out certain groups and make ads just for them.
Both geofencing and geotargeting help you find people by where they are, but your goals decide which one is best.
Business Types
The kind of business you have matters when picking geofencing or geotargeting. Stores, restaurants, and places with real locations do best with geofencing. You can reach people when they are close to your shop. For example, you can run sales for people within two miles or send messages for curbside pickup. Geofencing lets you make ads that fit the place and can even bring people from other stores.
Geotargeting is good for small businesses that want to reach bigger areas, like a whole city. You can mix location with what people like or do. For example, you can show ads for vegan pizza to people who like vegan food in one part of town. Geotargeting helps you not waste money on people who do not care and lets you try new places. You can see how your ads do in each spot and make your plan better.
Use geofencing when:
Restaurants want to offer quick deals or pickups
Businesses want fast, local contact
Use geotargeting when:
Small businesses want to grow in new places
Brands want to mix location with interests or habits
Companies want to run ads on Google or Facebook without needing location permission
Both geofencing and geotargeting help with location ads, but you need to pick the one that fits your business and who you want to reach.
Budget and Compliance
How much money you have and rules you must follow matter when picking geofencing or geotargeting. Geofencing costs more because it uses exact location data and needs setup and care. You might pay to start, pay each month, and buy special tools or software. These costs can be a few hundred or even thousands of dollars. Geofencing also costs more each time someone sees or clicks your ad because you target fewer people.
Geotargeting is cheaper. It uses general location info like IP addresses or zip codes. You pay less to set up and keep it running. Each time someone sees or clicks your ad, it costs less because you reach more people. If you do not have much money, geotargeting helps you get the most from your budget.
Aspect | Geofencing | Geotargeting |
|---|---|---|
Budget Requirement | Costs more because it uses exact location and needs setup | Cheaper, uses bigger areas like IP or zip codes |
Cost per Impression (CPI) and Cost per Click (CPC) | Higher because you target fewer people | Lower because you reach more people |
Setup and Maintenance | Needs money to start, monthly fees, and tools | Cheaper to start and keep running |
Suitable For | Best for businesses with more money who want exact ads | Good for businesses with less money who want to reach more people |
You also need to think about privacy and rules. Geofencing can make people worry about who owns their data and if it is safe. You must get clear permission before you collect location info. There are rules you must follow so you do not break the law or treat people unfairly. Tech teams often warn about safety risks with geofencing. You need to make rules and plans to keep data safe before you start.
Important rules to follow:
Keep people’s info private and do not share it without asking
Let people say no and hide their info to keep it safe
Tell people how you use their data in simple words
Use strong passwords and locks to stop others from getting in
Note: You must balance getting good results with keeping people’s info safe and following the law. You need to earn trust and do what the rules say.
Both geofencing and geotargeting are strong ways to use location in ads. Your money, business type, and rules will help you pick. You can start small, test your ads, and change your plan to get the best results.
Combining Geofencing and Geotargeting
When to Use Both
You can get better results by using geofencing and geotargeting together. This works well if you want to reach lots of people and also get quick action at certain places. For example, you can tell many people about your store in a big area. Then, when someone gets close to your store, you can send them a special deal.
Here are some times when using both is helpful:
You launch a new product and want everyone in a city to know. Geotargeting shows ads all over the city. When people get near your store, geofencing sends them a special offer.
You run a fast-food chain and want to reach people within ten miles. Geotargeting helps you show ads to those people. When someone walks near or enters your restaurant, geofencing gives them a mobile coupon.
You want your campaign to be more accurate. You use foot traffic data and ads on different channels. This makes your marketing work better.
This way, you get the wide reach of geotargeting and the quick contact of geofencing. You can make more people know your brand and also get them to act fast.
Real-World Examples
Many big brands have done well by using geofencing and geotargeting together. Here are some ways brands use these tools:
Burger King’s ‘Whopper Detour’ campaign geofenced McDonald’s locations. This helped them get over one million app downloads in a few days.
Dunkin Donuts used geo-conquesting to target other stores. They saw 36% of users click on offers and 3.6% use coupons.
Starbucks sends push notifications with deals when customers are near their stores.
Sephora’s app tells users about special offers and tips when they enter a geofenced area near a store.
Whole Foods got a 4.69% post-click conversion rate, which is three times the retail average, by using geofencing.
These examples show that using geofencing and geotargeting together can help you get more people interested, sell more, and bring more visitors to your business.
You can easily tell geofencing and geotargeting are not the same. The table below shows what each one does best:
Aspect | Geofencing | Geotargeting |
|---|---|---|
Scope | Finds people in one place | Uses location and info about users |
Best For | Talking to people right away | Reaching more people with special ads |
Setup | Easy to set up for one spot | Needs more work and info about people |
Pick your plan by thinking about your goals, who you want to reach, and how much money you have. Many people say using both geofencing and geotargeting is smart. Try different ways to see what helps your business most and change your plan as you learn.
FAQ
What is the main difference between geofencing and geotargeting?
Geofencing finds people who go into or out of a certain place. Geotargeting looks for people in bigger spots, like whole cities or zip codes. Geofencing is good when you want to reach someone right away. Geotargeting works better for ads that need to reach lots of people.
Can you use geofencing and geotargeting at the same time?
Yes, you can use both at once. Geotargeting helps you talk to many people in a big area. Geofencing lets you send messages to people close to your store. Using both can help more people know about your brand and act fast.
Is geofencing safe for user privacy?
You have to follow privacy rules and ask before tracking someone. Always tell people how you use their data. Keep their information safe and let them say no if they want.
Which method costs less for small businesses?
Geotargeting is usually cheaper for small businesses. It lets you reach more people in big areas for less money. Geofencing costs more because it needs special tools and is more exact.
How do you measure success with location-based ads?
You can count how many people visit your store or use coupons. You can also check how many people click on your ads. Use tools to see which plan brings in more customers and sales.
See Also
Using Thermal Imaging Cameras Effectively For Rescue Missions 2025
Key Developments Influencing Android Auto Wireless Adapters Today
Comparing Wireless CarPlay Adapters And AI Boxes For Value
Best Wireless Android Auto Adapters Reviewed And Compared 2025
Reviewing Leading Motorcycle GPS Units Featuring CarPlay And Android Auto
