
In-bus screen advertising is becoming increasingly popular as the market rapidly expands. The global bus infotainment system market, which includes in-bus screens, was valued at $483.4 million in 2023 and is projected to more than double by 2033.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Market Size 2023 | $483.4 million |
Projected Market Size 2033 | $1,113.3 million |
CAGR (2024-2033) | 8.7% |
This strong growth indicates a rising number of users and demonstrates the effectiveness of this advertising method. Brands carefully consider the investment cost and return when deciding to use in-bus screen ads. They also evaluate audience engagement and compare these factors to traditional advertising options before making a choice.
Key Takeaways
In-bus screen advertising shows ads to many people every day. The ads are bright and change often, so they get noticed and help people remember brands. Digital screens cost more at first, but they let you update ads easily. They also help you see how well ads work and get people more interested than old bus ads. Picking busy bus routes helps more people see the ads. This makes it more likely the right people will see them and helps you get more for your money. New technology like GPS and touchscreens lets you change ads right away. It also lets riders use fun features, so they pay more attention. Businesses that want local branding, to promote events, or reach lots of people get the most from in-bus screen advertising.
Is In-Bus Screen Advertising Worth It?
Key Considerations
Advertisers and brands look at many things before picking in-bus screen advertising. These things help them see if this method works well and is worth the money.
Strategic Placement and Targeting: Companies pick bus routes that reach certain groups of people. This helps the ads show up for the right viewers.
Dynamic Visuals and Interactivity: Digital screens use moving pictures, bright colors, and fun features like QR codes or augmented reality. These things grab attention and make people want to interact with the ad.
Content Localization: Advertisers often change messages for local areas. Local content feels more important and can get better reactions.
Frequency and Repetition: Buses go on the same routes every day. People see the ads many times, so they remember the brand.
Measurement and Analytics: Digital screens let advertisers count views, clicks, and actions. This information shows how well each campaign works.
Cost-Effectiveness: In-bus screen advertising usually costs less than old types of media. It is also better for the environment and can be changed easily.
Creative Storytelling: Good stories and surprises help ads stand out. Some brands work with local influencers to reach more people.
Real-Time Updates: Digital screens can change ads right away. This keeps the ads new and interesting.
Advertisers use different ways to see if their ads work. The table below shows how they track brand awareness and customer interest:
Metric | Description | Example/Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Impressions | How many times people might see an ad, based on how many walk or drive by. | A bus stop ad near a busy mall could get 10,000 views each day. |
Reach | How many different people see the ad. | 3,000 different people pass by a bus stop ad every day. |
Engagement | How people interact with the ad, like scanning a QR code or visiting a website. | 150 QR code scans from 10,000 views (1.5% engagement rate). |
Conversion Rate | The percent of people who do what the ad asks, like buying something or signing up. | 50 purchases from 150 people who interacted (33.3% conversion rate). |
Cost Per Impression | How much it costs for each view, by dividing ad cost by number of views. | $200 ad cost / 10,000 views = $0.02 CPI. |
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The total cost to get a new customer. | $1,000 campaign cost / 50 new customers = $20 CAC. |
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) | How much money is made for each dollar spent on ads. | $1,500 from 50 customers / $1,000 ad cost = 1.5 ROAS (150%). |
Advertisers also use tools like geofencing and QR codes to see how many people interact with ads. Surveys and research help check if people remember the brand. Social media and website data show if ads bring more online visits. Geo-tracking links ad views to visits in stores or other places.
Tip: Brands that use bright visuals, clear action steps, and good tracking tools often get the best results from in-bus screen advertising.
Market Trends
The in-bus screen advertising market is growing as cities add smart technology. Some trends are changing how these ads work:
Cities now have bus shelters that use solar power and can be changed easily. These shelters often have digital screens, Wi-Fi, and live bus info.
Many cities use AI, IoT, and GPS in buses. This helps show ads to the right people at the right time and makes riding better.
Cities and companies work together to pay for new digital screens and smart shelters. This gives cities and transit groups more money.
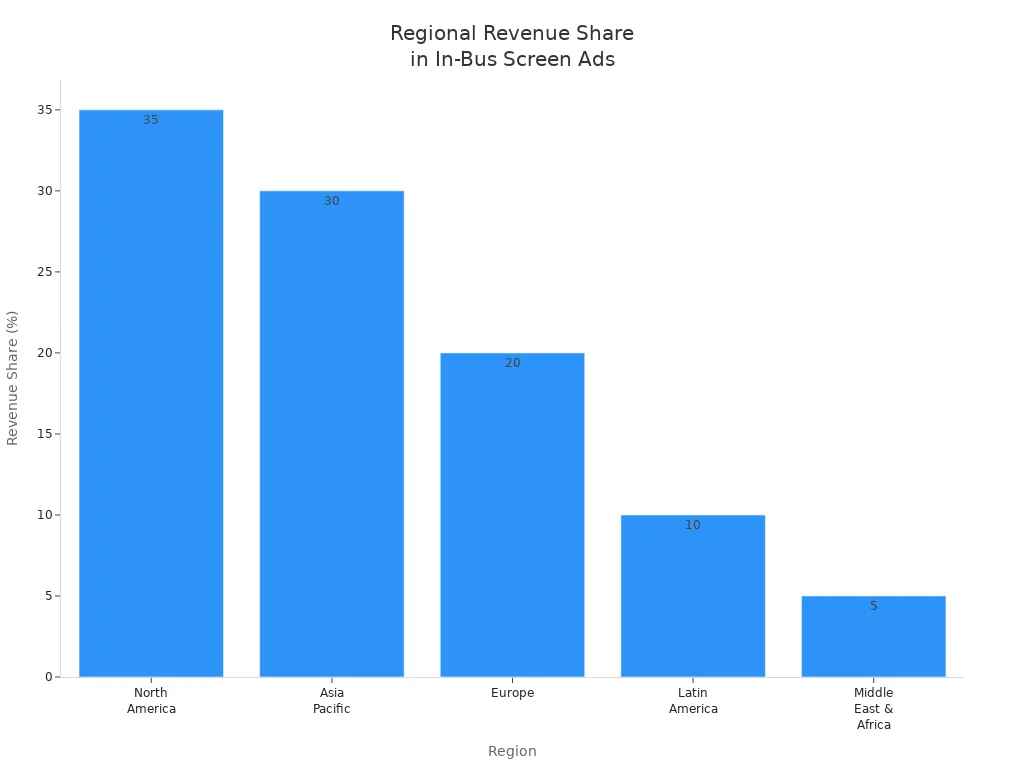
Asia-Pacific is growing fastest because cities are getting bigger and governments spend more on smart projects. North America and Europe are updating old systems with greener choices.
Advertisers use AI to learn what passengers like and show them special ads.
Being green is important. Many shelters use solar power and materials that can be recycled to help the planet.
The table below shows important market trends and differences in each region:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Market Share by Display Type | LED Displays: 45% (biggest share in 2023), LCD Displays: 35%, Others: 20% |
Fastest Growing Display Type | LCD Displays (because they look better and cost less) |
Key Applications | Public Transport (Buses & Trains) has the biggest share; school buses are growing fastest |
Regional Revenue Contribution | North America: 35%, Asia Pacific: 30%, Europe: 20%, Latin America: 10%, Middle East & Africa: 5% |
Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific (because cities are growing and more people use public transport) |
Market Size & Growth | USD 1.2 Billion in 2024; expected USD 2.5 Billion by 2033; CAGR ~8.9% (2026-2033) |
Growth Drivers | More people living in cities, smart city plans, government help, better technology |
Challenges | High starting costs, repairs, tech problems, keeping data safe, training workers |
Technological Trends | Using GPS, IoT, AI, live updates, and screens that save energy |
Regional Focus Examples | Europe (London, Paris using EU money), Asia Pacific (India, China spending a lot) |
In-bus screen advertising keeps changing with new technology and how people travel. Brands that know these trends and focus on good placement, creative ads, and strong tracking can get the most value for their money.
What Is In-Bus Screen Advertising?
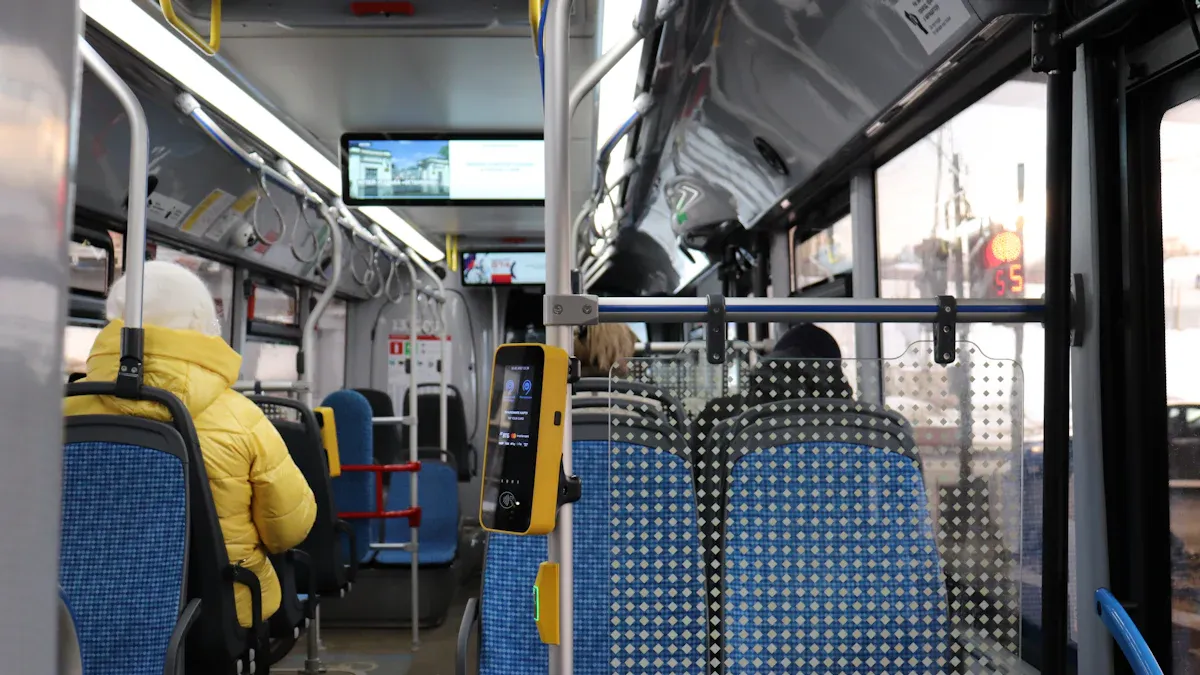

How It Works
In-bus screen advertising uses digital screens inside buses. These screens show ads, information, and fun videos. The screens are bright and clear, even during the day. Most use LCD or LED technology. Some screens are as big as 15.6 inches. They can play full HD or 4K video. Many screens use Android-based systems and have touchscreens. Passengers can touch the screen to interact with it.
Modern in-bus screens connect to Wi-Fi, GPS, and sometimes 4G. This lets the screens update ads right away. The ads can change based on where the bus is. For example, a restaurant ad might show up when the bus is close to that place. Some buses have two screens. One screen shows route info, and the other shows ads. This helps riders know where they are and see promotions at the same time.
Note: GPS helps these screens give real-time updates. Riders can see next-stop info and arrival times. This makes the trip easier for everyone.
The table below shows common tech used in in-bus screen advertising:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Display Type | LCD, LED, or TFT screens |
Operating System | Android-based |
Connectivity | Wi-Fi, GPS, optional 4G |
Video Support | 1080P, 4K, H.264/H.265 formats |
Touchscreen | Capacitive touch for interactivity |
Content Management | Dynamic, real-time updates |
Common Uses
Transit agencies and advertisers use in-bus screens in many ways. The main use is to show digital ads. These ads can be videos or moving pictures. The ads change during the ride and can match the time or place.
In-bus screens also show route info, like next stops and maps. Passengers see messages from bus companies or city leaders. Sometimes, screens show news, weather, or short shows to keep riders interested.
Advertising: Brands show products and services with bright pictures.
Route Information: Passengers get updates about stops and routes.
Public Messages: Officials share safety tips or event news.
Infotainment: Riders watch news, weather, or fun videos.
This mix of content keeps riders informed and entertained. It also helps advertisers reach people while they ride the bus.
Investment Cost and Return

Initial Costs
The first thing to think about is how much it costs to start. Digital in-bus screens cost more at the beginning than posters or wraps. Companies have to buy the screens and pay for putting them in. They might also need to buy special software. Posters and wraps are cheaper to make and put up. But digital screens can change ads fast and show new things any time.
The table below shows how static ads and digital screens are different:
Advertising Format | Initial Cost | Content Flexibility | Engagement Level | Maintenance Costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Static Bus Ads (Posters, Wraps) | Lower upfront production cost | Static, fixed content | Moderate, constant presence | Possible extra maintenance |
Digital In-Bus Screens | Higher cost for tech and install | Dynamic, easy updates | Higher engagement, interactive | Ongoing maintenance needed |
Digital in-bus screens need more money at first. This means buying screens, setting them up, and teaching workers. Static ads just need to be printed and put on the bus. If a company does not have much money, static ads might look better. But digital screens can show lots of ads and change them fast.
Note: Digital screens cost more, but they get more attention and can change ads easily.
Ongoing Expenses
After setting up, companies still have to pay for some things. Digital in-bus screens need to be cleaned and fixed sometimes. They also need new software and updates to stay safe. These things can cost more as time goes on. Static ads do not need much care, but changing them means printing new posters.
Ongoing costs for digital screens are:
Cleaning and fixing screens
Updating software and keeping it safe
Paying for electricity
Fixing or replacing broken screens
Static ads only need new posters when the ad changes. This takes time and work. Digital screens can change ads right away, which saves time and makes less trash.
Tip: Companies should think about both starting and ongoing costs before choosing.
Revenue and ROI
The main reason to run ads is to make more money than you spend. Digital in-bus screens usually give a good return on investment. Data shows that digital transit ads can give back 5% to 15% more money. This is better than many old types of ads.
For example, bus wraps and billboards do not get as much attention. They cannot change ads fast or see how well ads work. They may be cheaper at first, but they are not as flexible. Digital screens can show new ads all day and reach more people.
Ad Format | Average ROI (%) | Content Update Speed | Cost Per Impression | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Digital In-Bus | 5-15 | Instant | Low | 5-7 years |
Bus Wraps | 2-7 | Slow (manual) | Moderate | 1-2 years |
Billboards | 3-8 | Slow (manual) | Moderate | 2-5 years |
Digital in-bus screens last longer than posters or wraps. Most screens work for five to seven years. Over time, each view costs less because more people see the ads. Companies can also count how many people see and interact with the ads. This makes it easier to know if the ads are worth the money.
Companies using digital in-bus screens can reach more people, change ads fast, and see results better than with old ads.
ROI Factors
Location Impact
Where buses go is very important for ad success. If buses drive through busy city areas, more people see the ads. Picking routes with lots of people helps more people notice the ads. Brands pick routes that go where their customers are. This helps them reach the right people and get better results.
Buses in cities and suburbs show ads to many people. This helps more people see the brand.
Ads on busy routes get seen a lot. This helps people remember the brand.
Busy routes show ads to many, but buses move fast. People may only see ads for a short time.
These ads are easy to see, but it is hard to track results. Because buses move, people only see ads for a little while. This can make it harder for people to pay attention. Still, picking the best routes is key to getting good results.
Audience Reach
In-bus screen ads reach many different people every day. Riders can be students, workers, tourists, or families. This helps brands share their message with all kinds of people. City routes have the most riders, so ads reach more people there.
Bus ads reach people of all ages and backgrounds.
People who ride every day see the same ads a lot. This helps them remember the brand.
City and suburb routes have different people. Brands can pick the best route for their needs.
Ads reach many people, but not always the right group. More people may know the brand, but not everyone will care about the ad.
Content and Technology
Good ad content helps people notice and trust the ad. Bright pictures and moving videos get more attention. Brands that use simple words and clear messages do better. Ads that talk about local things or events get more people to look.
Cool designs and bright colors make ads stand out.
Changing ads often keeps them new and interesting.
Big letters and strong colors help everyone read the ads.
Funny or touching stories make ads easy to remember.
New tech like touchscreens and live updates help brands change ads fast. Testing and tracking tools show which ads work best. These tools help brands keep ads fun and useful, so they get better results.
Comparing Alternatives
Digital vs. Traditional Transit Ads
Digital in-bus screen advertising is very flexible. It lets companies target certain people. Companies can pick pay-per-click or pay-per-impression plans. This helps them control how much they spend. Digital ads can change right away and are easy to update. Advertisers can see how many people view or click the ads. This makes it simple to check if ads work well. Traditional transit ads like posters need more money at the start. These ads do not change until someone replaces them. This means printing and putting up new ads costs more over time. It is hard to know if these ads work because they do not give real-time data.
Digital ads help companies budget better and track results. Traditional ads show the same message but do not let people interact much.
Bus Screens vs. Billboards
Bus screens and billboards both show ads to lots of people. But they work in different ways. Bus screens show ads to riders while they travel. The ads can change based on where or when the bus is. This makes people pay more attention and lets brands send special messages. Billboards use one picture and stay in one place. They are easy to see but cannot change fast or let people interact. Bus screens can have things like QR codes. These let people do something right away.
Feature | Bus Screens | Billboards |
|---|---|---|
Content Updates | Real-time, dynamic | Manual, static |
Targeting | High (location/time) | Low (broad area) |
Engagement | Interactive options | Limited interaction |
Tracking | Real-time analytics | Estimated exposure |
Other OOH Options
Other out-of-home (OOH) ads include digital kiosks, mall screens, and ride-share screens. These use digital tech to show ads to the right people. They can change ads quickly to match what is happening. Digital OOH ads help brands reach people at important times, like when they travel or shop. Advertisers can change ads for weather, events, or who is around. This helps ads work better and saves money. These ads can also work with other digital tools, making them even stronger.
OOH ads are moving to digital. Digital ads are more flexible, easier to measure, and let brands be more creative than old types of ads.
Challenges
Tracking Effectiveness
Advertisers have a hard time knowing if in-bus screen ads work. Many things can change the results, like the bus route or how many people ride. The time of day also matters. Advertisers use different ways to check if ads are working:
1. They guess how many people see the ads by looking at where the bus goes and how busy it is. 2. They count QR code scans, promo code uses, and social media posts about the ad. 3. They check if people buy things or sign up using special codes or survey answers. 4. They try out different ad designs to see which one works best. 5. They think about who rides the bus, what time it is, the weather, and other ads on the bus. 6. They use tools and surveys to look at data right away and from before. 7. They look at important numbers often to change plans and make ads better next time.
Advertisers who do these things can learn what works and make better ads in the future.
Regulatory Issues
In-bus screen advertisers must follow many rules that are different in each city. In North America, there are lots of city and state laws and rules about what ads can show. These rules are not the same everywhere, so planning ads is harder and costs more. Advertisers also have to make sure ads are safe and okay for everyone. These rules can change, so advertisers have to keep checking them. Getting permission to run ads can take a long time and needs extra work. Old buses might need new parts before screens can go in, which costs more money and time. Rules about what ads can say, where they go, and how long they play can make ads less creative and not as strong. Advertisers have to change their plans for each city, which makes big ad campaigns harder to do.
Engagement Concerns
It is hard to get riders to look at in-bus ads. Many people use their phones, listen to music, or talk to friends on the bus. This means they might not see the screens or care about the ads. Ads that are not bright or interesting are easy to ignore. Advertisers need to make ads that are colorful, clear, and fun to watch. They should also change ads often so they do not get boring. Using things like touchscreens or QR codes can help, but only if riders want to use them. Making ads about local places or events can get more people interested, but it takes more work and planning.
Recommendations
When to Invest
Businesses should use in-bus screen advertising to reach many people. This works well for companies that want lots of people to see their ads. In-bus screens stay in front of riders for a long time. People cannot easily ignore these ads. Local businesses can show ads in certain neighborhoods or cities. Buses move around, so ads can help with new products or events. This helps spread news in different places.
Out-of-home advertising, like in-bus screens, often brings good results. For every dollar spent, companies can make almost six dollars in sales.
Many campaigns can do well with in-bus screens:
New product launches need to get attention fast.
Event promotions, like concerts or sales, reach people on the go.
Public awareness campaigns by governments or non-profits.
Brands wanting to reach commuters, students, workers, and seniors.
Companies can mix physical ads with digital actions, like QR codes.
The table below shows which business goals work best with in-bus screen advertising:
Business Goal | In-Bus Screen Fit |
|---|---|
Local brand awareness | ✅ Excellent |
Broad demographic reach | ✅ Excellent |
Event or product promotion | ✅ Excellent |
Measurable conversions | ❌ Limited |
Highly targeted campaigns | ⚠️ Moderate |
Cost-sensitive campaigns | ⚠️ Moderate |
Tip: Companies with flexible budgets and goals about visibility or awareness will get the most from in-bus screen advertising.
When to Avoid
Some businesses may not do well with in-bus screen advertising. Companies that need to reach a very specific group may have trouble. Bus routes and times do not change much. If a campaign needs to reach only certain people, in-bus ads may not work. Businesses with small budgets should be careful. Digital screens and fixing them can cost a lot over time.
It can be hard to measure results. Companies that need exact tracking or conversion data may not find in-bus ads helpful.
Short campaigns or ones that need quick changes may not fit. Once an ad starts, it is hard to stop or change it fast.
Busy cities have lots of ads, so yours must be very creative.
Design limits and short viewing times make it hard to share big ideas.
Things like weather or broken screens can make ads harder to see.
Here are times when in-bus screen advertising may not be best:
The target audience is not the same as bus riders.
The campaign needs fast changes or lots of testing.
The marketing budget is very small.
The business needs to track every click or sale.
The message is hard to understand and needs more time.
In these cases, companies should look at other ways to advertise that give better targeting, more flexibility, or easier ways to measure results.
In-bus screen advertising helps brands get noticed by many people. It works best on busy bus routes with lots of riders. Companies should think about how much they spend and what they get back. Ads should be short and use bright pictures to catch attention. Using data helps show ads to the right people. Advertisers can use new DOOH technology and show messages for certain places. They can add things like QR codes so people can interact with the ad. Brands that try new ideas and check how people react will do better over time. If a campaign needs lots of people to join in, using in-bus screens with other ad types can help even more.
FAQ
How much does in-bus screen advertising usually cost?
Most campaigns cost $500 to $2,000 each month for one bus. The price changes based on the city, screen type, and how long the ad runs. Digital screens cost more at first but are easier to change and track.
Can advertisers track how many people see their ads?
Advertisers use ridership numbers, GPS, and digital tools to guess how many people see ads. They also count QR code scans and website visits. It is hard to get exact numbers, but digital screens give better data than posters.
What types of businesses benefit most from in-bus screen ads?
Local stores, event planners, and brands that want to reach commuters do well with these ads. Companies that want lots of people to know about them or local events often pick this kind of ad.
How long do digital in-bus screens last?
Most digital screens work for five to seven years. Cleaning and updating software helps them last longer.
Are in-bus screen ads effective for brand awareness?
Yes. In-bus screens reach thousands of riders every day. Seeing the ads many times helps people remember brands. Bright pictures and simple messages make people pay more attention.
See Also
Budget-Friendly Portable CarPlay Solutions Suitable For All Drivers
Best Five E90 CarPlay Displays To Fit Any Budget
Why You Should Consider AI Box CarPlay In 2025
Comparing The Top CarPlay Dongles That Support Netflix
Helpful Tips For Using Apple CarPlay Wireless Adapters In Jaguars
